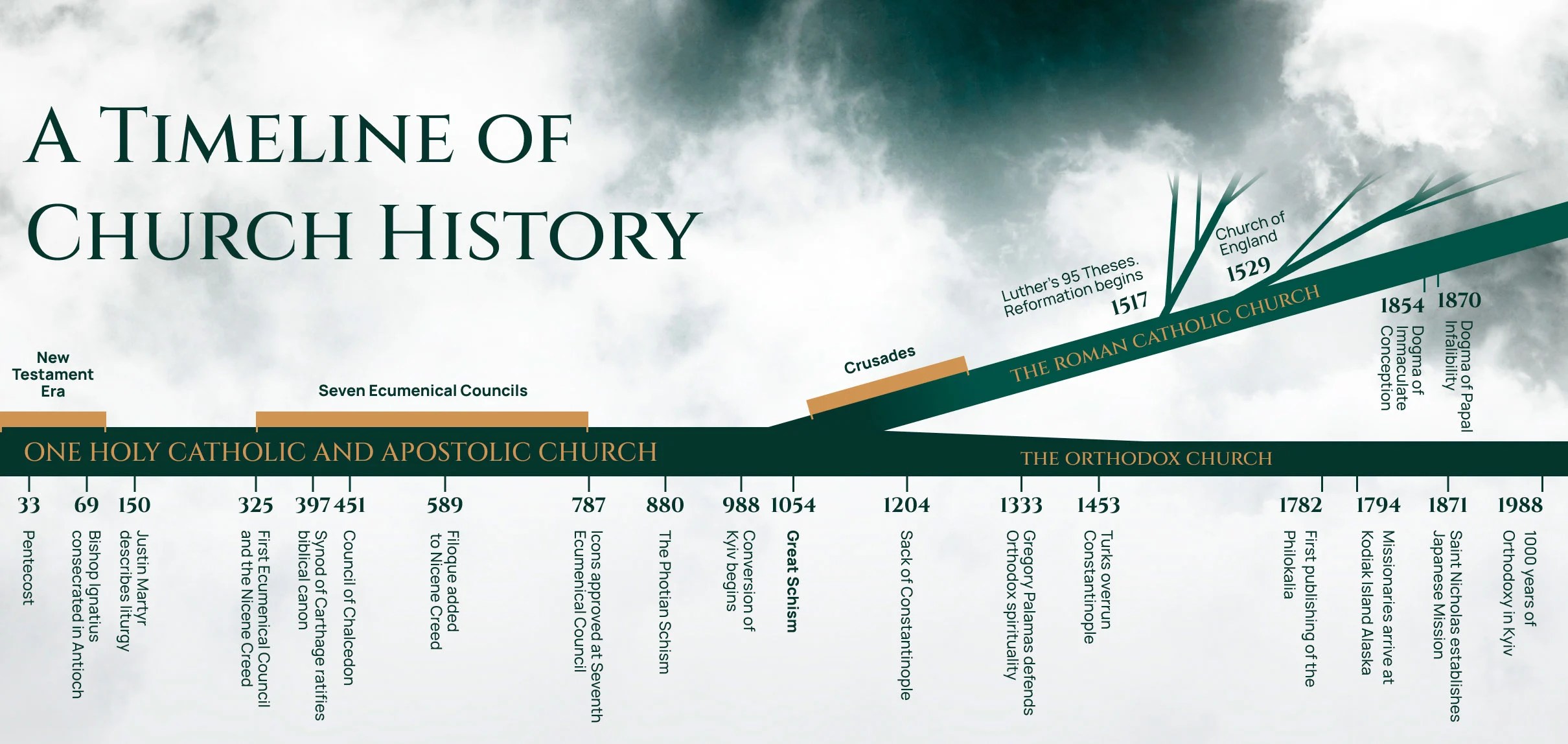
History
Theology the authorities can work with
Predictably, secular authorities convinced by the reformers’ truth claims liked the distinction drawn between the necessity of obedience to them and of disobedience to Rome. They liked hearing “the Gospel” accompanied by such “good news”—it would allow them, for starters, to appropriate for themselves all ecclesiastical property, including the many buildings and lands that belonged to religious orders, and to use it or the money from its sale in whatever ways they saw fit. In two stages during the late 1530s, seizing for himself the vast holdings of all the hundreds of English monasteries and friaries, Henry VIII would demonstrate how thoroughly a ruler could learn this lesson without even having to accept Lutheran or Reformed Protestant doctrines about grace, faith, salvation, or worship.
Brad S. Gregory, The Unintended Reformation
The long shadow of Puritanism
Long after Puritans had become Yankees, and Yankee Trinitarians had become New England Unitarians (whom Whitehead defined as believers in one God at most) the long shadow of Puritan belief still lingered over the folkways of an American region.
David Hackett Fischer, Albion’s Seed
Human Rights
Most menacing of all was the United Nations. Established in the aftermath of the Second World War, its delegates had proclaimed a Universal Declaration of Human Rights. To be a Muslim, though, was to know that humans did not have rights. There was no natural law in Islam. There were only laws authored by God.
Tom Holland, Dominion.
That’s pretty terrifying if Holland is correct and if a lot of Muslims are still faithful to that command ethic.
Salvation (“Soteriology”)
Hacking Eternity
I’m glad the authors or editors at Dispatch Faith came up with that “Hacking Eternity” title for a little bit of musing on Scott Adams’ (creator of Dilbert) self-reported deathbed conversion. It’s perfect:
For whatever reason, Adams delayed his conversion … In that January 4 X post, only nine days before his death, Adams said, “So I still have time, but my understanding is you’re never too late.” His final message, read by his first wife after his death, confirmed his plans: “I accept Jesus Christ as my Lord and Savior … I have to admit, the risk-reward calculation for doing so looks so attractive to me. So here I go.”
I cannot categorically rule out the sincerity of Scott Adams’ “conversion,” but with all the Pascal’s wager trappings, and delaying claiming Christ as Lord until the very last minute (when the formulaic Lordship carried no practical meaning, no period of following Christ’s example or commandments) I can’t not put conversion in precatory quotes, either.
I recall one classmate in my Evangelical boarding school who declared his intent to become a Christian some day, but not before he’d whooped it up as much as possible. Last I knew, he was whooping it up at age 50+ with pneumatic wife #2. His declaration was so consistent with the logic of evangelical soteriology (study of salvation) pervasive in that time and place that the only refutations I can recall were:
- That he might be murdered, or have a fatal car collision, or otherwise die too suddenly to effectuate his last minute “conversion.”
- That refusing salvation for too long risked “hardening of the heart” to where could not repent.
Better would be this, I think, though it would probably be dismissed as “works righteousness”:
Be not deceived; God is not mocked: for whatsoever a man soweth, that shall he also reap. For he that soweth to his flesh shall of the flesh reap corruption; but he that soweth to the Spirit shall of the Spirit reap life everlasting.
Yeah, that’s a proof-text, taken without context. But I’d still say it fits.
The current milieu
The denominations
A new era of martyrdom
The Episcopal Church of New Hampshire is ready for frickin’ war. The Episcopalians are amped up. Bishop Rob’s reflection from earlier this month: “We are now, I believe, entering a time, a new era of martyrdom.” Of his priests: “And I’ve asked them to get their affairs in order—to make sure they have their wills written, because it may be that now is no longer the time for statements, but for us with our bodies to stand between the powers of this world and the most vulnerable.” These guys are not kidding around anymore. They are ready to die. And there will be cookies after the sermon.
Nellie Bowles. Bishop Rob’s letter has to be seen to be disbelieved. It features an ecclesiology straight from the lowest-church fever swamps:
As soon as the Christian church became linked to the empire by Constantine in the year 325 or so, the church immediately became corrupt.
(Italics added)
Ummmm, that’s just not credible. I don’t even think that educated clergy of low-church persuasion would defend that if pressed. To hear it from a Bishop of a high church is shocking but evocative. After all, what authority does a corrupt church have to tell Bishop Rob,
a man of profound historical privilege, … one who has made statements that, [he has] to say, have been really good and eloquent,
that he can’t innovate like mad to drive out that millenia-long corruption?
I’m still trying to figure out if “Rob” is his last name or if it’s an aw-shucks affectation. (Googles the question) Of course: it’s affectation.
Ostensibly Protestant; functionally, what?
There is another obvious fact that few denominational Protestants in the SBC or PCA seem willing to admit: The growth in these ostensibly traditional denominations stems almost entirely from the work of the Non-Denom churches. As already mentioned, pan- or pseudo-denominational organizations now own the church planting space. All church plants, to a great extent, utilize the methods and mores of Non-Denom Church. Most no longer even have their host denomination in their names. Therefore, I wager that whatever growth exists in the SBC and PCA is almost entirely the result of the Non-Denom churches growing within the husk of the world of traditional Protestantism.
Casey Spinks, Does Traditional Protestantism Have a Future?
Christianity and nationalism
Christianity does not simply fade away with the rise of nationalism; the process is more one of the reconfiguration of Christian elements to fit within a nationalist framework. When the holy migrates from the church to the nation-state, the church does not disappear but generally takes a supporting role to the creation of national identities.
William T. Cavanaugh, The Uses of Idolatry
The nondenominations
Nondenominational Protestantism
Douthat: Right. But I’m going to ask you to generalize. … For people who aren’t familiar with that world, what is nondenominational Protestantism right now?
Burge: They’re evangelical. Not all of them, but the vast, vast majority are evangelical in their orientation and theology and practice and all the things that we would call evangelical.
One thing is, they’re anti-institutional. They’re anti-authority in a lot of ways. Where does your money go when you put it on the plate? Well, it goes right here. It stays right here in these four walls. So what we’re going to have is a very fragmented Protestant Christianity, where you’ve got a little fiefdom here of 15,000 people in this church, and 20,000 people in this church.
I think the problem is, it’s going to be harder to conceptualize, to measure, to really understand what these groups look like, because now you’ve got these little pockets. You’ve got Joel Osteen in Houston, Texas. He’s an evangelical, but he doesn’t interface with most other evangelicals. You got Paula White down in Florida, whom Trump loves, but she’s Pentecostal and believes in the gifts of the spirit. And other evangelicals, like Franklin Graham, would never talk to Paula White.
You’ve got all these little pockets, and they don’t add up to a cohesive “What is evangelicalism?” In 30 years, that question is going to be almost impossible to answer. Not that it’s easy now, but it’s going to be 10 times harder because of this amorphous nature of nondenominationalism.
Ross Douthat and Ryan Burge (shared link). Ryan Burge is the most interesting social scientist focused on religion that I know. The transcript of his podcast is worth reading in full; I both listened and then read, highlighting heavily.
For my money, “amorphous” and “fiefdom” are the keys to nondenominational evangelicalism, and the two are related. The substantive religious content of the nondenominational religious landscape is amorphous, despite the shared term “evangelical,” because they are individual fiefdoms. The pastors may well be untutored and unorthodox, and they certainly are unaccountable to any higher authority.
But be careful: Burge leaves the impression, inadvertently I think, that these nondenominational churches typically number in the thousands. I’d be surprised if the median number of members or attenders was as high as 200. Burge no doubt would know the numbers on that if asked directly.
Orthopathos
Because of the divorce from the historic Church, Evangelicalism has sought for a new way to satisfy the need for materiality. This is why such believers have welcomed pop music and rock-n-roll into their churches. It is why emotion is mistaken for spirituality. It is why sentiment is substituted for holiness. Sincere feeling is the authenticator. Instead of icons of Christ, whose piercing stare calls you to repentance, the Evangelical can go to a Christian bookstore and buy a soft-focus, long-haired picture of Jesus. He’s a “nice” Jesus, but it is hard to believe that He is God.
Fr. Andrew Stephen Damick, Orthodoxy and Heterodoxy
I bang on a lot about Evangelicalism, my former affiliation, and specifically about the difficulty of defining it so as to be able to say “no, that’s not evangelical.” Ken Myer, founder of Mars Hill Audio Journal, once offered the possibility that while evangelicals don’t really share a coherent common doctrine, an orthodoxy, that they do share a common feeling or sentiment, an “orthopathos.”
Christianity Today
Sometime within the past year, I subscribed to Christianity Today. It is a magazine whose founding described it as “A fortnightly journal of evangelical persuasion” or something very like that.
I thought very highly of it. Just as I was an Intervarsity Christian Fellowship guy instead of a Campus Crusade for Christ guy, so I was a CT guy instead of a Moody Monthly guy. I even wrote a very cringe item they published. (I’ll give you no further hints whereby to unearth it.)
By and large, CT today has been a big disappointment, and I do not intend to renew.
The main part of the disappointment has been less the content of their articles (which certainly need a critical filter for evangelical bias), but the banality (it seems to me) of the topics of their articles. We’re just not remotely on the same wavelength any more. This “dumbing down” began nearly 50 years ago, and even then I took that as a sign that the evangelical appetite for chewing on meaty topics was waning.
But Thursday past, they finally floated on their RSS feed a story the topic and timeliness of which got my attention: How to Know If You’re Growing in Patience—or Just Giving Up.
Yes, it should be “whether” instead of “if,” but I’ll not dwell on that. It just seems to me as we, to whatever degree, watch the ICE terrorism and murders in Minneapolis, powerless to do anything, the spiritual line between patience (with prayer and trust in God’s providence) and giving up is an important one.
Jaw-dropping nadir
Majorities of white evangelicals favor deporting undocumented immigrants to foreign prisons in El Salvador, Rwanda, or Libya without allowing them to challenge their deportation in court (57 percent), and approve of placing immigrants who have entered the country illegally in internment camps (53 percent).
“It has become virtually impossible to write a survey question about immigration policy that is too harsh for white evangelicals to support,” Robert P. Jones, the president of the Public Religion Research Institute, recently wrote.
Tobias Cremer is a member of the European Parliament. His book The Godless Crusade argues that the rise of right-wing populism in the West and its references to religion are driven less by a resurgence of religious fervor than by the emergence of a new secular identity politics. Right-wing populists don’t view Christianity as a faith; rather, Cremer suggests, they use Christianity as a cultural identity marker of the “pure people” against external “others,” while in many cases remaining disconnected from Christian values, beliefs, and institutions.
…
The Trump administration has gone one step further, inverting authentic Christian faith by selling in a dozen different ways cruelty and the will to power in the name of Jesus. It has welcomed Christians into a theological twilight zone, where the beatitudes are invoked on behalf of a political movement with authoritarian tendencies. This isn’t the first time in history such things have happened.
…
Huge numbers of American fundamentalists and evangelicals—not just cultural Christians, but also those who faithfully attend church and Bible-study sessions and prayer gatherings—prefer the MAGA Jesus to the real Jesus. Few of them would say so explicitly, though, because the cognitive dissonance would be too unsettling. And so they have worked hard to construct rationalizations. It’s rather remarkable, really, to see tens of millions of Christians validate, to themselves and to one another, a political movement led by a malignant narcissist—who is driven by hate and bent on revenge, who mocks the dead, and who delights in inflicting pain on the powerless. The wreckage to the Christian faith is incalculable, yet most evangelicals will never break with him. They have invested too much of themselves and their identity in Trump and what he stands for.
Sacraments or notions?
Christianity that has purged the Church of the sacraments, and of the sacramental, has only ideas to substitute in their place. The result is the eradication of God from the world in all ways other than the theoretical.
Fr. Stephen Freeman, Everywhere Present
Orthodoxy
Rescue
He is Jesus, the name chosen before his birth. The angel spoke separately to Mary and Joseph, and told them that the baby’s name would be Jesus, “because he will save his people from their sins” (Matthew 1:21). The name Jesus means, in Hebrew, “God will save.” When Gabriel says “he will save his people” the Greek verb sozo means “save” as in rescue, like “saved you from drowning.” That kind of “saved,” not “intervened and paid your debt.”
I had been a Christian decades before it occurred to me that this means Jesus can rescue us from our sins, not merely from the penalty for our sins. He can free us from the sins themselves. We will still fail over and over to take his outstretched hand and be lifted from the mire. We like mire. But he can do it, and make us not merely debt-free in his Father’s sight, but transformed and filled with his light.
Repentance
Repentance is everything you do to get sin, those inborn passions, out of you. It’s reading, thinking, praying, weeding out disruptive influences in your life, sharing time with fellow Christians, following the guidance of the saints. Repentance is the renunciation of what harms us and the acquisition of what is beneficial to us, writes a holy counselor.
Dee Pennock, God’s Path to Sanity
A glimpse into an Orthodox mind
The Protoevangelium of James is not a text that itself holds a position of authority in the life of the Church. Indeed, the West formally rejected it well before the Great Schism. Nevertheless, the Church preserved the text through centuries of copying and recopying. It stands as the earliest written witness to the antiquity of a number of important traditions related to the New Testament Scriptures regarding the lives of the Theotokos, St. James, and their family. The Protoevangelium of James did not originate these traditions, nor does it provide their authority. Their authoritative form exists in the liturgical life of the Church, in hymnography and iconography.
Fr. Stephen DeYoung, Apocrypha (bold added).
All the well-educated Orthodox teachers agree on this. If you hear an Orthodox layman answer “How do you know that?” with “We get it from the Protoevangelium of James,” know that s/he’s got that backwards.
Darkness and Light
As Stephen Wormtongue Miller pronounces from the White House that the way the world works is by force, I’m very glad to be in a church where every Sunday we sing the Beatitudes, which tell us the way blessedness works.
Religious ideas have the fate of melodies, which, once set afloat in the world, are taken up by all sorts of instruments, some woefully coarse, feeble, or out of tune, until people are in danger of crying out that the melody itself is detestable.
George Elliot, Janet’s Repentance, via Alan Jacobs
[N]one of the things that I care about most have ever proven susceptible to systematic exposition.
Alan Jacobs, Breaking Bread With the Dead
You can read most of my more impromptu stuff here and here (both of them cathartic venting, especially political) and here (the only social medium I frequent, because people there are quirky, pleasant and real and it has no-algorithms). All should work in your RSS aggregator, like Feedly or Reeder, should you want to make a habit of it.